Options for Reducing the Revenue Loss of TCJA Extension
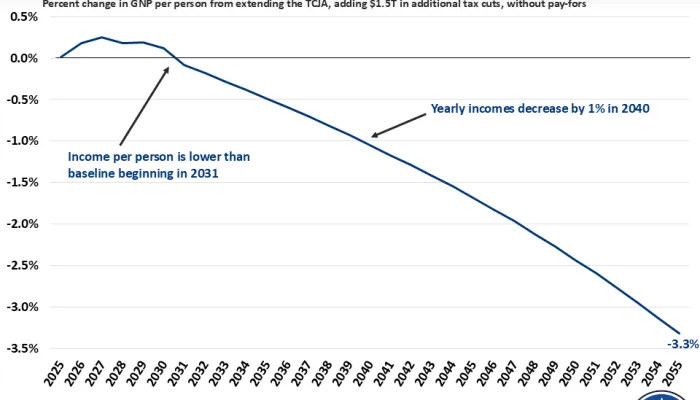
Extending the individual and estate provisions from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) expiring at the end of next year without offsets would add $3.9 trillion ($4.5 trillion with interest) to deficits through Fiscal Year (FY) 2035, at a time when debt is already approaching record levels and climbing unsustainably.
Policymakers should pursue deficit reduction next year, and at the very least ensure any tax cuts or spending increases – including extensions – are fully offset to avoid worsening the fiscal outlook. An important opportunity to do this is to ensure that TCJA extensions are part of a deficit-reducing bill.
Many organizations have put forth fully offset tax plans, and others can make their own with our Build Your Own Tax Extensions tool.
The table below includes numerous options to lower the deficit impact of any TCJA extension (with options described and revenue estimated relative to full extension). These could be coupled with additional revenue measures or spending cuts, including many that have been or will be outlined in our new Budget Offsets Bank.
Note: these options are based on the FY 2026-2035 budget window; savings would likely be 15 percent less over the FY 2025-2034 budget window, varying by option. Savings are estimates based on CBO scoring, are rounded to the nearest $5 billion, and are subject to change based on policy specification.
The table below is a menu of options and does not represent recommendations from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, its board, or its staff.
Options for Reducing the Deficit Impact of TCJA Extensions
Sources: Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget and CRFB adjustments of estimates from Congressional Budget Office, Joint Committee on Taxation, Internal Revenue Service, Department of the Treasury, Tax Foundation, Pomerleau-Schneider, Bipartisan Policy Center, Yale Budget Lab, and Penn Wharton Budget Model as well as underlying estimates from Solutions Initiative 2024 plans (using scores from Tax Policy Center) from American Enterprise Institute, Manhattan Institute, Bipartisan Policy Center, and American Action Forum.
* Represents very rough estimates
’ This would involve adjusting the AMT rates to achieve specific revenue collection targets.
The figures above are not additive – both because some are mutually exclusive and because there are many interactions. But one could put together a combination of policies to extend elements of the TCJA on a roughly revenue-neutral basis, either while extending all the tax rate cuts or nearly all elements of the TCJA (without adjustment) except for the rate cuts. Users can also design their own extension using our Build Your Own Tax Extensions tool.
Importantly, the options above only include changes to the TCJA itself and closely related policies. Many more revenue options beyond these changes could also help finance any extensions or reduce deficits, as could spending cuts. See our Budget Offsets Bank for some examples.
Within the TCJA, one place to start might be with the family-related provisions. The TCJA eliminated the personal and dependent exemptions and, in their place, doubled the Child Tax Credit (CTC) to a partially refundable $2,000 per child, made the CTC available to those higher on the income ladder, and nearly doubled the standard deduction to $15,000 per adult by 2025. While we estimate extending these changes would add about $300 billion to the deficit over a decade, they could actually reduce deficits if the CTC and standard deduction were phased out at lower income levels, the standard deduction was expanded a bit less, or the Head-of-Household filing status was scaled back. For example, further means-testing the CTC and standard deduction could reduce the deficit impact by nearly $300 billion and eliminating the Head-of-Household status could save a similar amount on top of that.
Lawmakers could also let certain minimum taxes return in part or in full. The TCJA repealed the “Pease” surtax on itemized deductions, and it repealed the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for all but about 300,000 taxpayers by increasing the AMT’s income requirement and exemption amount. Extending these changes would increase deficits by roughly $800 billion. Restoring Pease or AMT in some form could recover some of that revenue loss.
On the offset side, the TCJA capped the state and local tax (SALT) deduction at $10,000, reduced the cap on the mortgage interest deduction from $1 million to $750,000, and repealed various other smaller deductions – which could help raise a combined $1.6 trillion if extended. Lawmakers could raise hundreds of billions more by expanding this base broadening. For example, fully eliminating the SALT deduction for all individuals and businesses would raise an additional $800 billion on top of extending the cap; simply closing an existing workaround to the cap would raise about $200 billion. Meanwhile, reducing the mortgage interest cap to $500,000 and limiting the charitable deduction to cash donations would raise a combined $400 billion.
Broader itemized deduction changes could raise even more revenue. For example, full repeal of all itemized deductions would reduce the deficit impact of extension by nearly $1.2 trillion. Or limiting the value of itemized deductions to the 24 percent tax bracket – essentially capping the percentage value of deductions for those making over $200,000/$400,000 – would raise roughly $250 billion on top of TCJA extension. That cap could raise around $500 billion if applied more broadly.
Changes to pass-through and other business provisions could also reduce the deficit impact of extension. The TCJA enacted a pass-through deduction that allows owners of pass-through entities to deduct up to 20 percent of qualified business income, expanded the Opportunity Zone program that offers tax preferences for investing in certain economically distressed communities, and limited the amount of losses businesses can deduct. Extending these provisions would reduce revenue by a combined $800 billion over a decade. Replacing or reforming these provisions – something tax experts on the left and right have supported – could recover hundreds of billions of dollars.
Reforms to the estate tax could also save money relative to full TCJA extension. The TCJA doubled the estate tax exemption from $5.5 million per person in 2017 to $11.2 million in 2018, growing to $14 million by 2025. Extending this would reduce revenue collection by $190 billion. This revenue could be replaced in full by adopting a carryover basis, instead of stepped-up basis, for capital gains at death. It could also be recovered by modifying estate tax parameters. For example, reverting the estate tax parameters to the 2018 levels set after the TCJA was enacted – with a $11.2 million per person exemption – could reduce the revenue loss of extension by roughly $80 billion if parameters were frozen at that level. Closing various loopholes that allow people to avoid the estate tax could generate another $50 billion.
Finally, lawmakers could choose not to extend all the individual rate cuts under the TCJA. A full extension would reduce revenue by $3.4 trillion – and therefore represents most of the net impact of TCJA extension. Setting rates midway between current law and TCJA could reduce that revenue loss nearly in half, setting the top rate to 39.6 percent for income above $400,000 would reduce it by roughly $650 billion, and simply freezing all the existing inflation-indexed provisions in the tax code for two years could reduce it by roughly $700 billion.
Once decided on their preferred tax base, lawmakers could set rates wherever they want to achieve their desired revenue and distributional goals.
Putting the federal budget on a sustainable path already requires tough choices against current law, choices that would become much more challenging with an extension of the TCJA because it would worsen the fiscal outlook significantly. Delaying action will result in taxpayers bearing the consequences of interest on a growing government debt load and slower economic growth.
If lawmakers plan on extending the TCJA, a pro-growth and fiscally responsible plan is critical to the nation’s well-being. That should involve carefully considering which parts of the TCJA are worth keeping, which are worth changing, and how to at least fully offset whatever revenue loss remains.
Note (01/31/2025): This blog has been updated to reflect new estimates by the Congressional Budget Office, Joint Committee on Taxation, Bipartisan Policy Center, the Department of the Treasury, and Penn Wharton Budget Model since publication.